Financial Education for Market Women Programme (FEMWP)

Several national governments and international organisations have financial inclusion as a developmental priority. This is in a bid to create a nexus between financial inclusion and the poor.

Several national governments and international organisations have financial inclusion as a developmental priority. This is in a bid to create a nexus between financial inclusion and the poor.
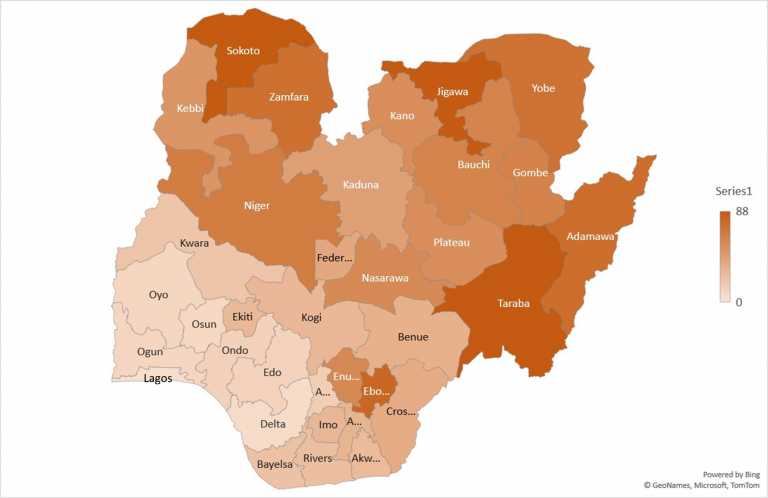
The NLSS, on analysis revealed that about 82.9 million citizens in Nigeria (40.1 percent) of about 200 million are regarded ‘’Poor” in a period spanning between September 2018 and October 2019.

The strategies, routines or techniques applied by the Federal Government of Nigeria and other development partners towards this achievement could be replicated on several other national health goals such as reduction of infant mortality rates, improve access to primary health care through expansion of the National health insurance scheme (NHIS) among others. These emphases are crucial to avoiding any setbacks and sustaining this achievement.
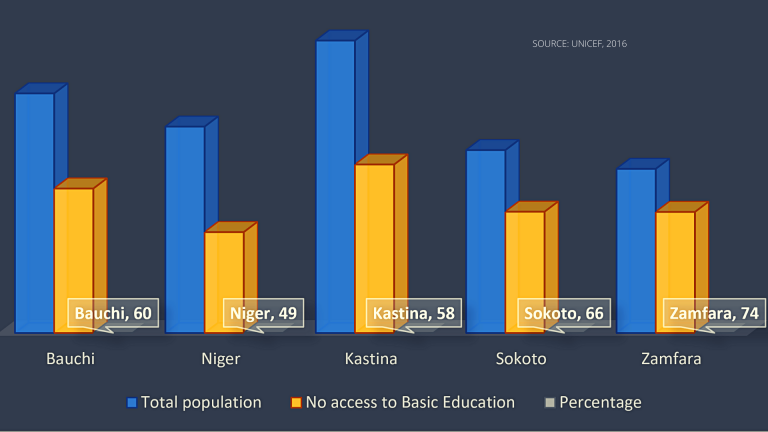
The impact of COVID-19 has exposed the uncertainties of most economies worldwide, especially those of developing nations like Nigeria. The reduction in oil revenue due to the COVID-19 pandemic could prevent Nigeria from achieving its financial targets for 2020.